About Heart Failure
The Heart
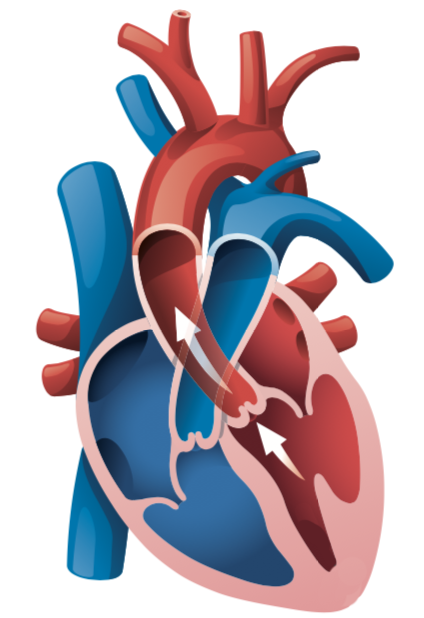
The heart is a muscular organ in your chest and is about the size of a closed fist. Its primary purpose is to pump blood to the rest of the body. The heart pumps blood following an electrical signal that causes a contraction of the heart. The heart is divided into four chambers which include the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
The left ventricle is the most important chamber in the heart as it is responsible for supplying a sufficient amount of blood to the rest of the body’s organs. It is important that it is functioning properly to support the overall well-being of the body.
What is a Heart Attack?
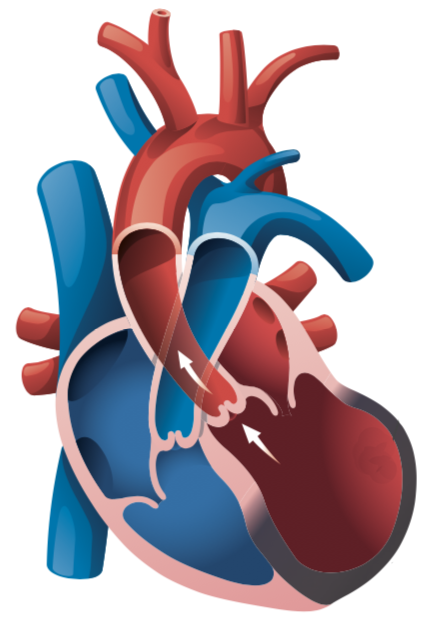
A heart attack is caused by a narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries which supply blood to the heart. This causes structural damage to the heart’s left ventricle.
Two problems that may occur to the left ventricle after a heart attack are scarring and dilation, which if not treated, will eventually lead to a heart failure.
Heart Failure Symptoms
As a result of your heart attack, the heart may pump an insufficient amount of blood to the body from a failing heart. You may experience the following symptoms:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Reduced ability to perform physical activity
- Lightheadedness
- Fluid in the lungs and swelling in the legs
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Heart Failure Medication
These medications each perform a specific function to help you feel better, but they will not cure your heart failure. Your doctor may have you on one or more of the following medications:
- ACE inhibitors: lowers blood pressure and increases the amount of blood your heart pumps
- Digoxin: slows heart rate in patients with atrial fibrillation
- Beta blockers: manages abnormal heart rhythms and protects the heart from having another heart attack
- Diuretics: helps relieve fluid and swelling that may occur as a result of your heart failure